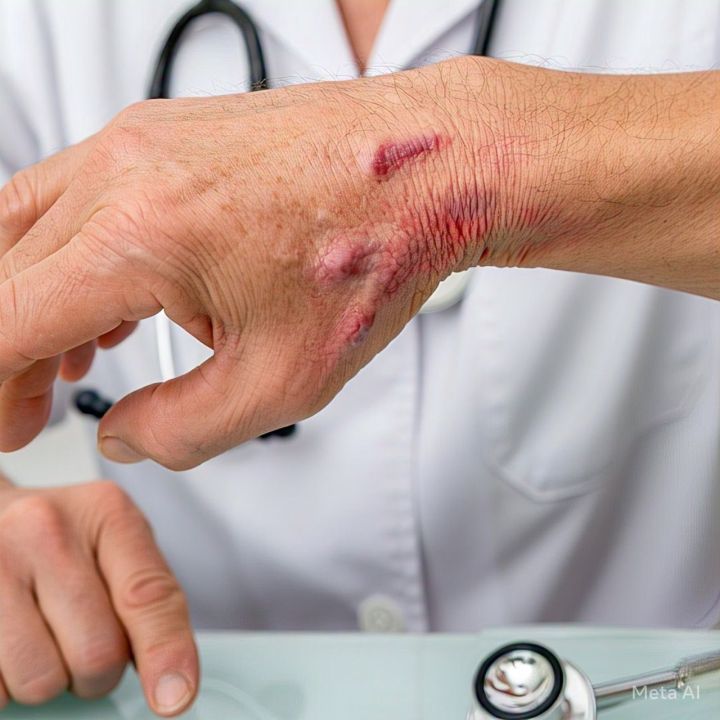
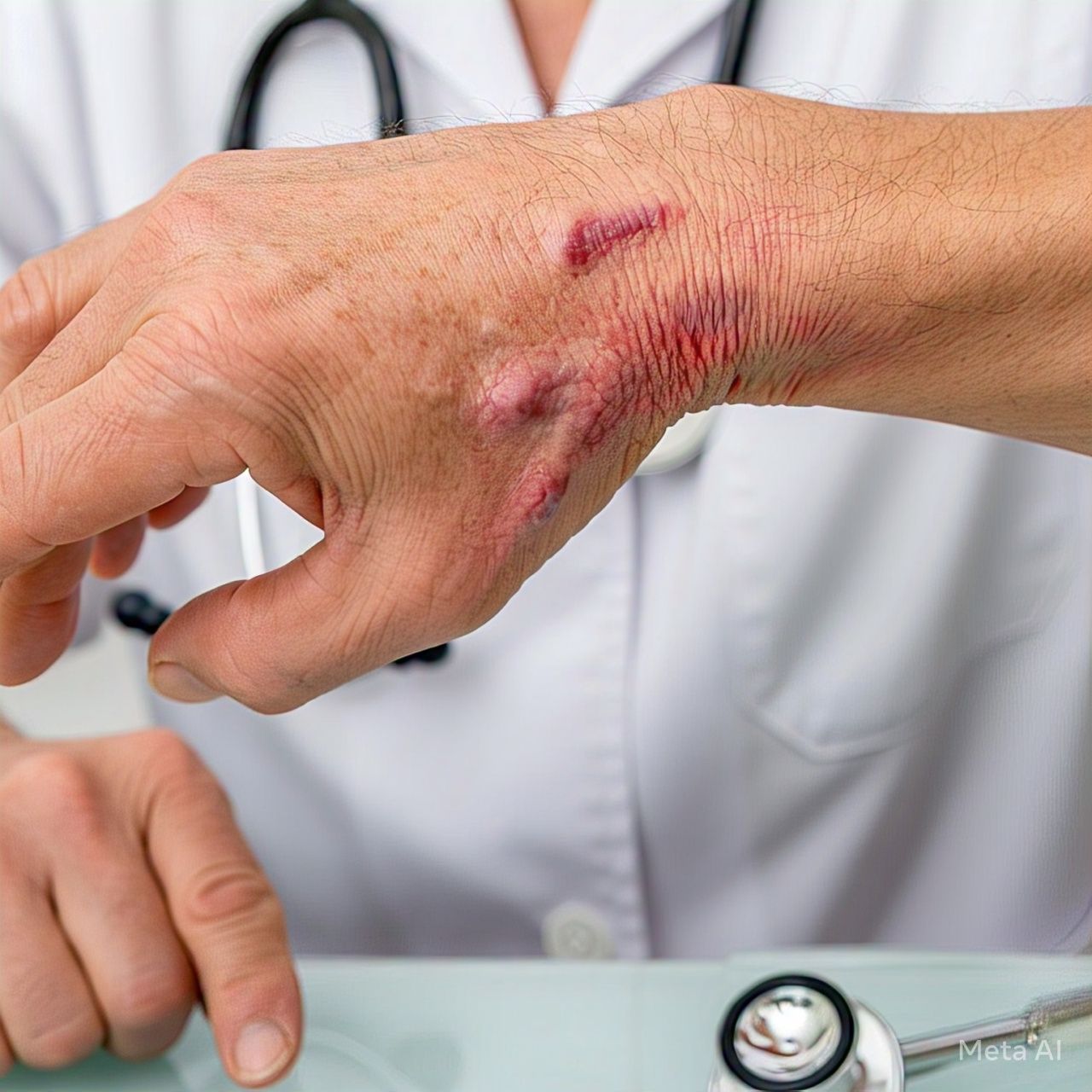
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic inflammatory disorder that primarily affects joints. Unlike osteoarthritis, which occurs due to wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune condition. This means the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks its own tissues, including joints, causing painful swelling that can eventually result in joint deformity and erosion.
In this comprehensive blog post, we will explore everything you need to know about rheumatoid arthritis, including its symptoms, causes, diagnosis, treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and the latest research on this debilitating condition.
What is Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Rheumatoid arthritis is a systemic autoimmune disease, meaning it can affect more than just joints. It may also involve the skin, eyes, lungs, heart, and blood vessels. The inflammation associated with RA can damage various body systems, making early diagnosis and aggressive treatment crucial.
RA affects approximately 1% of the global population and is more common in women than in men. The disease usually begins between the ages of 30 and 60, but it can occur at any age.
Symptoms of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The signs and symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis may vary in severity and can come and go. The most common symptoms include:
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Management
- Joint pain and tenderness
- Stiffness, especially in the morning or after inactivity
- Swollen joints
- Fatigue
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
RA typically affects smaller joints first, such as those in the fingers and toes. As the disease progresses, it can affect larger joints, including the knees, hips, shoulders, and elbows.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of rheumatoid arthritis is unknown, but several factors may contribute to its development:
- Genetics: Certain genes may make some people more susceptible to RA.
- Environmental triggers: Smoking, infections, and exposure to certain chemicals may trigger RA in those genetically predisposed.
- Hormones: Because RA is more common in women, hormonal factors might play a role.
- Age: Although RA can affect people of all ages, it most commonly starts between the ages of 30 and 60.
- Family history: Having a family member with RA increases your risk.
Diagnosing Rheumatoid Arthritis
Early diagnosis is key to managing RA effectively and preventing joint damage. Doctors use a combination of tests and criteria to diagnose RA:
- Medical history and physical exam
- Blood tests: These include rheumatoid factor (RF), anti-CCP antibodies, ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate), and CRP (C-reactive protein).
- Imaging tests: X-rays, MRIs, and ultrasounds can detect joint damage and inflammation.
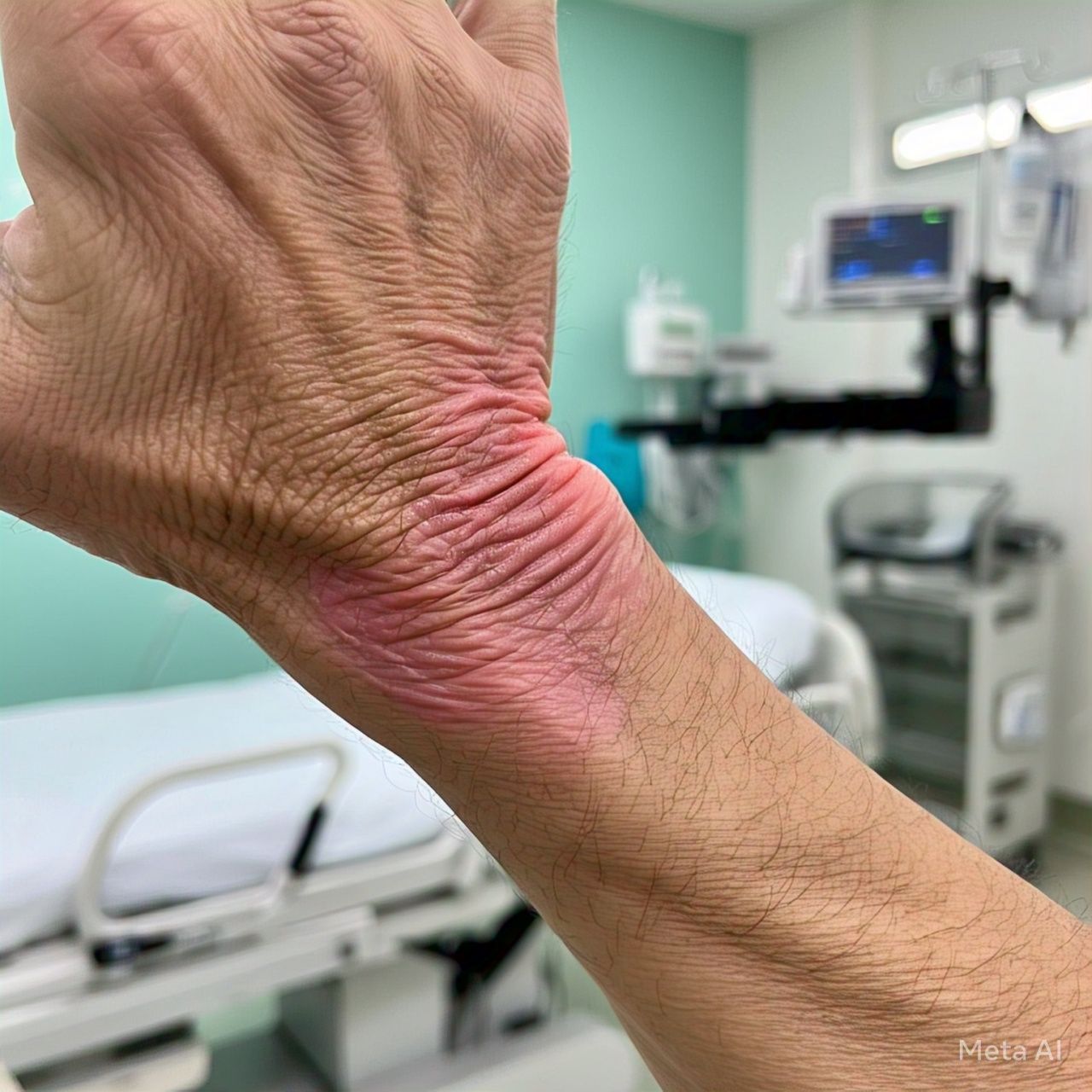
Treatment Options
Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Management
There is currently no cure for rheumatoid arthritis, but treatment can help manage symptoms and prevent joint damage. Treatment plans are usually tailored to the individual and may include:
1. Medications
- NSAIDs: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve pain and reduce inflammation.
- Corticosteroids: These are fast-acting drugs that can reduce inflammation quickly.
- DMARDs: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs can slow the progression of RA and save joints and tissues from permanent damage.
- Biologic agents: These target specific parts of the immune system and are often used when traditional DMARDs don’t work.
2. Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can improve flexibility and strengthen muscles around the joints, reducing the overall strain and improving function.

Understanding Rheumatoid Arthritis: Symptoms, Causes, and Management
3. Lifestyle Changes
- Regular exercise: Low-impact activities such as swimming, walking, and yoga can help maintain joint flexibility.
- Healthy diet: Anti-inflammatory foods, such as leafy greens, fatty fish, nuts, and whole grains, can help reduce symptoms.
- Quit smoking: Smoking increases the risk and severity of RA.
- Weight management: Maintaining a healthy weight reduces stress on joints.
Living with Rheumatoid Arthritis
Living with RA can be challenging, but many people lead fulfilling lives with proper management. Here are some practical tips:
- Listen to your body: Rest when you’re tired. Overexertion can lead to flare-ups.
- Stay organized: Keep a symptom diary to track triggers and effectiveness of treatments.
- Join a support group: Connecting with others can provide emotional support and practical advice.
- Work with your healthcare team: Regular checkups with your rheumatologist are essential.
Complementary and Alternative Therapies
Some people find relief using complementary therapies, though these should never replace conventional treatment:
- Acupuncture
- Massage therapy
- Supplements: Omega-3 fatty acids, turmeric, and vitamin D are commonly used.
- Mind-body practices: Meditation, tai chi, and deep-breathing exercises can help manage stress.
The Future of Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatment
Advancements in medical research offer hope for better treatment options. Some promising areas include:
- Personalized medicine: Tailoring treatments based on genetic profiles.
- Stem cell therapy: Research is ongoing into regenerating damaged joint tissues.
- New biologics: More targeted drugs are being developed with fewer side effects.
Conclusion
Rheumatoid arthritis is a complex and often misunderstood condition. While it presents many challenges, early diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment plan can dramatically improve quality of life. Understanding the disease, staying informed about new treatments, and making healthy lifestyle choices can empower you to live well with rheumatoid arthritis.
If you suspect you may have RA or are experiencing persistent joint pain and swelling, consult a healthcare professional as soon as possible. With the right care, it’s possible to manage rheumatoid arthritis effectively.